Regulations Amending the Toys Regulations (Magnetic Toys): SOR/2018-138
Canada Gazette, Part II, Volume 152, Number 14
Registration
June 25, 2018
CANADA CONSUMER PRODUCT SAFETY ACT
P.C. 2018-870 June 22, 2018
Her Excellency the Governor General in Council, on the recommendation of the Minister of Health, pursuant to section 37footnote a of the Canada Consumer Product Safety Actfootnote b, makes the annexed Regulations Amending the Toys Regulations (Magnetic Toys).
Regulations Amending the Toys Regulations (Magnetic Toys)
Amendments
1 The definitions plush toy, soft toy and toy in section 1 of the Toys Regulationsfootnote 1 are replaced by the following:
plush toy means a toy with a raised fibre surface. (jouet en peluche)
soft toy includes a toy that is stuffed or made of pliable rubber or pliable plastic. (jouet mou)
toy means a product that is intended for use by a child under 14 years of age in learning or play. (jouet)
2 Section 37 of the Regulations is replaced by the following:
Shaft-like handle
37 A pull or push toy that has a shaft-like handle that measures 10 mm or less in diameter must have a protective tip that is placed on the end of the handle to prevent puncture wounds and that is able to withstand a pulling force of 44.5 N.
3 Subsection 38(3) of the Regulations is repealed.
4 The Regulations are amended by adding the following after section 42:
Magnetic Toys
Magnetic force
43 Every magnetic toy and any of its magnetic components, including those magnetic components that become separated from the magnetic toy or magnetic component when tested in accordance with Schedule 9, that can be totally enclosed in the small parts cylinder, as illustrated in Schedule 1, using a force of not more than 4.45 N, must have a magnetic flux index of less than 0.5 T2mm2, when tested in accordance with Schedule 10.
Exceptions
44 (1) Section 43 does not apply to the following magnetic components:
- (a) those that are necessary for the operation of motors, relays, speakers and other electrical or electronic components in a magnetic toy, provided that the magnetic properties are not part of the play or learning pattern of the toy; and
- (b) subject to subsection (2), those that are part of a kit intended for carrying out educational experiments involving both magnetism and electricity and intended for a child of at least 8 years of age.
Warning — container and instructions for use
(2) The following warning or its equivalent must be displayed prominently and legibly in English and French on the kit’s container and instructions:
WARNING!
Not suitable for children under 8 years of age. This kit contains small magnets. Swallowed magnets can stick together across intestines causing serious injuries. Seek immediate medical attention if a magnet may have been swallowed.
MISE EN GARDE!
Cette trousse ne convient pas à un enfant de moins de 8 ans. Elle contient de petits aimants. Les aimants qui sont avalés peuvent s’attirer mutuellement à travers l’intestin et engendrer ainsi de graves blessures. Consultez immédiatement un médecin si un enfant semble avoir avalé un aimant.
5 Schedule 1 to the Regulations is replaced by the Schedule 1 set out in Schedule 1 to these Regulations.
6 The Regulations are amended by adding, after Schedule 8, the Schedules 9 and 10 set out in Schedule 2 to these Regulations.
Coming into Force
7 These Regulations come into force on the day that, in the sixth month after the month in which they are published in the Canada Gazette, Part II, has the same calendar number as the day on which they are published or, if that sixth month has no day with that number, the last day of that sixth month.
SCHEDULE 1
(Section 5)
SCHEDULE 1
(subsection 7(1) and sections 30 and 43)
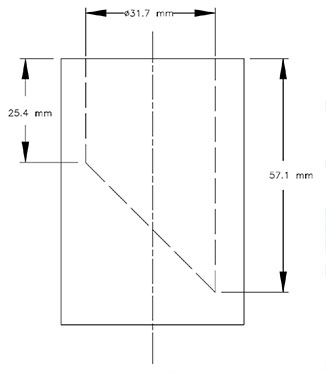
Small Parts Cylinder
SCHEDULE 2
(Section 6)
SCHEDULE 9
(Section 43)
Test Method for Integrity of Magnetic Toys and Magnetic Components
1 The following method is to be used for testing the integrity of magnetic toys and magnetic components:
- (a) in the case of a magnetic toy or magnetic component that is made of wood, that is intended to be used in water or that is brought into contact with the user’s mouth in order to be used, begin by completing the following steps:
- (i) submerge it for four minutes in a container of demineralized water that is maintained at a temperature of 21 ± 5°C,
- (ii) remove it from the water and shake off the excess water,
- (iii) maintain it at a temperature of 21 ± 5°C for 10 minutes,
- (iv) repeat steps (i) to (iii) three more times and proceed immediately to the next step;
- (b) subject to paragraph (c), place the magnetic toy or the magnetic component being tested near another magnetic component of that same toy or component using the orientation that creates the strongest magnetic attraction in the course of reasonably foreseeable use of the toy or component and allow them to connect then pull them apart to the distance where magnetic attraction ceases;
- (c) if the magnetic toy or the magnetic component cannot be tested without either of them breaking or if the toy or the magnetic component has only one magnet, place the magnetic toy or the magnetic component near a flat, circular reference disc with a minimum nickel content of 99%, a diameter of 30 mm and thickness of 10 mm using the orientation that creates the strongest magnetic attraction in the course of reasonably foreseeable use of the toy or component and allow them to connect then pull them apart to the distance where magnetic attraction ceases;
- (d) repeat the step described in paragraph (b) nine more times;
- (e) test the magnetic toy or the magnetic component according to the tests set out in the following sections of the ASTM International standard F963, entitled Standard Consumer Safety Specification for Toy Safety, as amended from time to time, in the order below, while ensuring that for toys for use by a child of at least 8 years of age, the criteria for children over 36 months in Table 5 entitled “Test Parameters for Use and Abuse Tests” and the weight criteria in section 8.7.1 of that standard are used:
- (i) section 8.7.1 “Drop Test”,
- (ii) section 8.7.2 “Tipover Test for Large, Bulky Toys”, as these toys are defined in that Standard and in which section “worst attitude” is replaced by “most onerous position”,
- (iii) section 8.8 “Torque Tests for Removal of Components”,
- (iv) section 8.9 “Tension Test for Removal of Components”,
- (v) section 8.25.4.6 “Impact Test”,
- (vi) section 8.25.4.7 “Compression Test”;
- (f) repeat step (b) 10 more times.
SCHEDULE 10
(Section 43)
Test Method for Determination of Magnetic Flux Index
Required Materials
1 The following materials are required for determining the magnetic flux index:
- (a) a direct current field Gauss meter with a resolution of 0.0005 T that is capable of determining the flux density of the magnetic field to a minimum accuracy of 1.5% and that has an axial type probe with an active area diameter of 0.76 ± 0.13 mm that is at a distance of 0.38 ± 0.13 mm from the probe tip; and
- (b) a caliper or similar device for measuring dimensions to a minimum accuracy of 0.1 mm.
Procedure
2 The following method is to be used for determining the magnetic flux index:
- (a) place the Gauss meter probe tip perpendicularly against the surface of the magnetic toy or the magnetic component and slowly move the probe across the entire surface to locate the maximum absolute value of the flux density;
- (b) record the maximum absolute value of the flux density in tesla;
- (c) extract the magnet by breaking the magnetic toy or magnetic component, if necessary, without damaging the magnet;
- (d) calculate in square millimetres the area of the biggest pole surface of the magnet using the geometric formula for the surface area that corresponds to the shape of the surface:
- (i) if the pole surface is flat, measure the dimensions with an accuracy of ± 0.1 mm,
- (ii) if the pole surface is not flat, as in (i), measure the dimensions of the maximal cross-section that is perpendicular to the axis that goes through the magnet poles with an accuracy of ± 0.1 mm,
- (iii) if the magnet is a multi-pole magnet, measure the dimensions of the largest single pole, which can be identified using magnetic field viewing film or an equivalent method;
- (e) square the maximum absolute value of the flux density and multiply it by the area of the biggest pole surface of the magnet to obtain the magnetic flux index, expressed in tesla squared millimetre squared.
REGULATORY IMPACT ANALYSIS STATEMENT
(This statement is not part of the Regulations.)
Executive summary
Issues: While magnetic children’s toys had been popular for decades and used without magnet-related health or safety concerns, around 2003 there was a proliferation in the use of small powerful magnets in toys. This resulted in reports of children of all ages ingesting them and suffering serious, life-threatening internal injuries. The small powerful magnets involved in these incidents were made of rare earth elements, and they had a much stronger power to attract to one another than magnets previously common in toys (such as ceramic magnets or flexible rubber magnets). Many rare earth element magnets are so powerful that if ingested they can attract across several layers of intestinal tissue. Some ingestion incidents have resulted in considerable damage to intestinal tissues and required emergency surgical treatment; in some cases, children face serious long-term health consequences.
To address this serious ingestion hazard, mandatory safety requirements for magnetic toys have been in place in the United States since 2008 and in the European Union since 2009. Health Canada (the Department) focused its early risk management efforts, starting in 2006, on providing safety information and advisories to inform and educate the public and the toy industry. Since 2013, Health Canada has considered certain magnetic toys to pose a danger to human health or safety within the meaning of the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act (CCPSA); therefore, their manufacture, import, advertisement or sale in Canada is prohibited. However, this policy is not reflected in Health Canada’s Toys Regulations (the Regulations).
Magnetic attraction continues to be a popular play feature in children’s toys. The regulatory amendments incorporating requirements and tests consolidate all magnetic toy requirements in an accessible, transparent and consistently applied manner.
Description: The amendments to the Regulations under the CCPSA include a restriction on both the size and the attractive strength of magnetic toys and magnetic components of toys, with consideration for functional magnets in electronic components and magnets contained in advanced experimental kits for older children. The amendments also set out a series of integrity tests to verify that dangerous magnetic components do not separate from a toy or its components when used.
Cost-benefit statement: A cost-benefit analysis (CBA) concluded that the amendments would have low economic costs, given that the majority of toy manufacturing occurs outside Canada and that the majority of magnetic toys available in Canada are likely to meet magnet-related toy safety requirements in place in the United States and the European Union. The total 10-year costs to industry of the amendments are estimated to be approximately $94,610 (present value, 2016 price level) for product redesign and annual testing.
In terms of benefits, the amendments are expected to result in fewer injuries to children, and they should decrease the need for medical attention or hospitalization by reducing the availability of dangerous magnetic toys. The total 10-year benefits are estimated to be approximately $2.4 million (present value, 2016 price level) based on a reduction in injuries and treatment costs. A sensitivity analysis was completed as part of the CBA. It demonstrated that if the present value of costs is five times higher than estimated and the present value of benefits is 80% lower than estimated (which could reflect a situation where the majority of magnetic toys on the market already meet the requirements outlined in Health Canada’s policy), a small net benefit of $15,000 over 10 years is still estimated.
The net benefit is estimated at $2.3 million over 10 years (2017 to 2026) [present value, 2016 price level].
“One-for-One” Rule and small business lens: The “One-for-One” Rule does not apply, since the amendments will not impose any administrative costs on industry. The small business lens does not apply, because the estimated nationwide cost impact of the amendments is less than $1 million per year.
Domestic and international coordination and cooperation: The amendments will align Health Canada’s safety requirements and tests for magnetic toys with those set out in law in the United States and the European Union.
Gender-based analysis plus: The amendments to the Regulations take into consideration that the small powerful magnet ingestion incident characteristics and injury pathways are the same for all children. The amendments help to protect children under 14 years of age from magnet ingestion hazards when they play with magnetic toys irrespective of their height, weight, age or gender. There is no additional cost associated for gender-based considerations.
Background
The Hazardous Products (Toys) Regulations came into force under the Hazardous Products Act in 1970 and were transferred in 2011 as the Toys Regulations (the Regulations) under the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act (CCPSA). Along with other provisions and regulations under the CCPSA, the Regulations help protect Canadian children from a wide range of hazards when they interact with toys. However, they do not currently reflect the Department’s view that certain magnetic toys pose a danger to human health or safety and are therefore prohibited.
A proliferation in the use of small powerful magnets in a wide variety of children’s toys began in 2003. These small powerful magnets were made of rare earth elements, and they had a much stronger power to attract to one another than magnets previously common in toys (such as ceramic magnets or flexible rubber magnets). Powerful magnets that are very small can be easily swallowed. The strength of these powerful magnets makes them capable of attracting each other through up to six layers of intestinal wall.footnote 2 The magnet ingestion hazard is considered a hidden hazard because the consequences of ingesting powerful magnets are not obvious. The early symptoms a child eventually develops resemble a stomach flu, and medical attention may not be sought until severe trauma has developed. The injury is even difficult for physicians to diagnose because of the flu-like symptoms. In 2005, a 20-month-old child in the United States died after ingesting magnets.footnote 3 Dozens of surgeries had already been performed in the United States by 2007.footnote 4
Due to the serious ingestion hazard posed by small powerful magnets in children’s toys, several jurisdictions, including Canada, have implemented risk management strategies to help reduce incidents. Initial risk management actions taken in the United States focused on public education and advisories. In addition, in the United States, voluntary safety requirements were established under the ASTM F963 toy safety standard, and these became mandatory in 2008. In the European Union, mandatory safety requirements were established under the EN 71-1 toy safety standard in 2009. The international ISO 8124-1 toy safety standard set out requirements for magnets in 2012. The magnet-related requirements across the current editions of these three standards are aligned.footnote 5, footnote 6, footnote 7
Similar to the United States, Health Canada focused its early risk management efforts, starting in 2006, on providing safety information and advisories to inform and educate the public and the toy industry about the serious ingestion hazard that small powerful magnets in toys pose to children. Health Canada has also
- conducted a consultation, before publication in the Canada Gazette, Part I, on proposed amendments to the Regulations regarding magnetic toys in 2009;
- updated its online Industry Guide to Health Canada’s Safety Requirements for Children’s Toys and Related Products, 2012 to include recommendations for magnetic toysfootnote 8 in 2012;
- determined, in 2013, that certain magnetic toys with powerful magnetic components that are small enough to be swallowed and capable of attracting across intestines pose a danger to human health or safety within the meaning of the CCPSA, and published this policy online as an information notice to industry;footnote 9 and
- distributed, in 2013, a letter to over 1 000 toy industry members explaining the determination and new policy that certain children’s toys containing small powerful magnets are a danger to human health or safety and that the manufacturing, import, sale or advertising of these products is a contravention of the general prohibitions set out in paragraphs 7(a) and 8(a) of the CCPSA.
Issues
Unlike other small objects that are more likely to pass normally through the digestive system if ingested, when more than one powerful magnet is ingested in a short period of time, the magnets can attract to one another while moving through the intestines. When magnets attract across tissues, they can twist the intestines and create a blockage or slowly tear through the intestinal walls.footnote 10, footnote 11 Some ingestion incidents have required emergency surgical treatment and have resulted in considerable damage to intestinal tissues; in some cases, children face long-term health consequences as a result of the injuries they sustained.footnote 12
Children swallow the powerful magnets in foreseeable ways during play, either intentionally or unintentionally. Young children are vulnerable to incidents because of their exploratory mouthing behaviour. Older children are vulnerable to incidents because the strength of magnetic attraction enables a multitude of creative play opportunities generally unrelated to the manufacturer’s intent for a toy. Incident reports indicate that older children swallow magnets when they mistake magnets for candy, use their teeth to separate magnets when building structures, attach magnets to their braces, attach magnets across their cheek, use the magnets to pretend to have a lip or tongue piercing, and use the magnets in other ways.footnote 13
In 2005, a 20-month-old child in the United States died after ingesting several powerful magnets that had separated from the plastic pieces of a magnetic toy building set.footnote 14 In April 2007, the United States Consumer Product Safety Commission was aware of at least 33 cases of children, aged 10 months to 11 years, ingesting powerful magnets and requiring emergency surgery to remove the magnets and repair damage to the intestines.footnote 15
Complete information on the number of non-fatal and fatal injuries to Canadian children involving small powerful magnets in toys is not available. Information on injuries involving magnets was provided by the Canadian Hospitals Injury Reporting and Prevention Program (CHIRPP). CHIRPP records are based on the collection and analysis of data on injuries to people (mainly children) who are seen in emergency rooms of participating hospitals in Canada. CHIRPP records, which cover a six-year period starting from 2005, indicate that of 327 magnet-related cases recorded, the most common injury was related to ingestion of one or more magnets (73%). Notably, the cases identified do not represent all injuries in Canada during that period, but only those seen at the emergency departments of the 16 hospitals in the CHIRPP network at the time. With respect to the patient age distribution, approximately
- 31% of cases involved children between 0 and under 3 years of age;
- 48% of cases involved children between 3 and under 8 years of age; and
- 20% of cases involved children between 8 and under 14 years of age.
In terms of patient outcomes, 53% of the cases required emergency room treatment, and 3% required hospital admission. Most of the cases that led to hospital admission involved magnet ingestion. No further specificity on the products involved, nature of injuries sustained, treatments or outcomes is available from the CHIRPP records.
In addition to the CHIRPP hospital data, Health Canada has received four direct reports of Canadian children ingesting magnetic toy components. In two of the cases, the children, aged three years and seven years, sustained no injuries. In 2008, a five-year-old child required emergency surgery to repair eight bowel perforations that resulted from ingesting two magnetic components from a building toy.footnote 16, footnote 17 In 2014, a three-year-old child ingested powerful magnetic components from a toy building set sold between 2006 and 2009. Fortunately, the child’s parent witnessed the swallowing of one component and they brought the child to the hospital where one of the components was removed non-surgically and the other passed uneventfully in the child’s stool.footnote 18
The CHIRPP data review was limited to six years starting from 2005, because around 2010, cases of ingestion of small powerful magnets or magnetic components from toys became difficult to distinguish from those involving magnets from novelty magnet sets. Around 2010, novelty magnet sets — which are considered to be those often marketed as desk toys and stress relievers for adults — became prevalent on the Canadian market. Despite generally being marketed to individuals 14 years of age and older, magnets from these sets found their way into the hands of children, followed by the same ingestion and injury pattern that was seen with small powerful magnets and magnetic components in toys.footnote 19, footnote 20
In 2013, the Department concluded an assessment of the risks posed by small powerful magnets and determined that some novelty magnet sets, and certain magnetic toys, pose a danger to human health or safety and are therefore prohibited under sections 7 and 8 of the CCPSA. In that year, Health Canada also completed a market survey of more than 100 retail outlets and identified over 700 unique magnetic toys being sold in Canada, demonstrating that magnetic attraction is a play feature that continues to be popular in children’s toys.
It is anticipated that the majority of magnetic toys on the Canadian market comply with the general prohibition in Canada and the mandatory safety requirements in place in the United States and the European Union. However, these jurisdictions still identify and remove non-compliant magnetic toys from their markets. For example, in 2016, the European Commission’s Rapid Alert System for dangerous non-food products published 16 recalls for toys containing dangerous magnets. The most recent Canadian recall involved dangerous magnetic toys that had been sold in Canada from July 2016 to October 2017footnote 21.
Currently, the Regulations, which are made under the CCPSA, do not include requirements to protect children from the serious ingestion hazard posed by certain magnetic toys. Some industry stakeholders may not be aware of the extent of their obligation to make their magnetic toys safe. There are also continued recalls in the United States and the European Union, where this is codified in rule.
Objectives
The objective of the amendments is to set out specific requirements under the existing Regulations that will help to protect children from the serious ingestion hazard posed by small powerful magnets in toys, consolidating the requirements with other Canadian safety requirements for toys. A further objective is to align Canada’s regulatory requirements and tests for this hazard with those applied in the United States and the European Union.
Description
The amendments set a requirement that any magnetic toy or magnetic component of a toy must either be too large to be likely to be swallowed or the magnet must not be so powerful that it can attract across intestines if swallowed. These requirements have to be met both before and after the toy or component is subjected to certain integrity tests intended to reveal potential weaknesses in how a magnet is contained in a toy or in the magnet’s structure. Exceptions are for magnets in electrical systems or those in advanced experimental sets intended for children eight years of age or older.
Specifically, the amendments to the Regulations include the following two principal elements:
- A requirement that any magnetic toy or magnetic component that can be entirely enclosed in the small parts cylinder must have a magnetic flux index of less than 0.5 T2mm2. The small parts cylinder is illustrated in Schedule 1 of the Regulations, and the test incorporates the use of a force of not more than 4.45 N. The method to assess the magnetic flux index is set out in a new schedule of the Regulations.
- A requirement stating that the above criteria must also be met after the magnetic toy or magnetic component is subjected to a standard series of integrity tests set out in a new schedule of the Regulations. The tests outlined in Table 1 are captured in the schedule. Note that for the drop, torque, tension, impact and compression tests, the ASTM F963 standard is referenced, as amended from time to time, to align tests for magnetic toys between Canada and the United States for current and future versions of ASTM F963.
Table 1. Summary of integrity tests for magnetic toys and magnetic components
Test |
Comparison or Referenced Standardsfootnote 22,footnote 23,footnote 24 |
|---|---|
Soaking test for magnetic components of wooden toys, toys to be used in water or toys brought into contact with the user’s mouth for use |
This test is described in the schedule and aligns with ASTM F963-17, section 8.25.4.1; EN 71-1:2014, clause 8.9; and ISO 8124-1:2018, clause 5.34. |
Initial tension test for magnets (10 attach-detach cycles) |
This test is described in the schedule and aligns with EN 71-1:2014, clause 8.34; and ISO 8124-1:2018, clause 5.31. It also aligns with ASTM F963-17, except with respect to the number of cycles (1 000 cycles is used in the ASTM standard). |
Drop test |
Incorporation by reference of ASTM F963-17, sections 8.7.1 and 8.7.2 |
Torque test |
Incorporation by reference of ASTM F963-17, section 8.8 |
Tension test |
Incorporation by reference of ASTM F963-17, section 8.9 |
Impact test for magnets |
Incorporation by reference of ASTM F963-17, section 8.25.4.6 |
Compression test |
Incorporation by reference of ASTM F963-17, section 8.25.4.7 |
Final tension test for magnets |
This test is described in the schedule and aligns with EN 71-1:2014, clause 8.34; and ISO 8124-1:2018, clause 5.31. It also aligns with ASTM F963-17, except with respect to the number of cycles (1 000 cycles is used in the ASTM standard). |
Small parts cylinder
The small parts cylinder is used to identify magnetic toys or magnetic toy components that are of a size that may be able to be swallowed. This cylinder is an internationally recognized gauge used to identify objects that pose ingestion or choking hazards to young children. The use of the small parts cylinder in magnetic toy safety requirements has been applied in the United States and the European Union.
Magnetic flux index
The magnetic flux index is a measure of the attractive power of a magnet. It is derived from the flux density, which is measured by a Gauss meter (with units in tesla squared [T2]), and the area of the pole surface of the magnet (with units in millimetres squared [mm2]). The amendments use 0.5 T2mm2 as the maximum limit of magnetic flux index, which is the full metric equivalent to the 50 kG2mm2 limit used in the United States and the European Union. The value is considered to provide a margin of safety to protect against magnets capable of attracting across intestinal tissue, given that rare earth element magnets can range in magnetic flux index values of between 2.0 and 3.5 T2mm2. In comparison, the magnets involved in the death of the child in 2005 had a 3.4 T2mm2 magnetic flux index.footnote 25
Toys with only one magnet
The amendments apply to toys with as few as one magnet, since one small powerful magnet in combination with another ferromagnetic object (such as most Canadian coins) could produce the same result of attracting across intestinal tissues if ingested.footnote 26 This approach aligns with magnetic toy safety requirements in the United States and the European Union.
Exceptions
The amendments establish two exceptions that align with those in the United States and the European Union. The first is an exception for a magnetic component that is required for the function of a motor, relay, speaker, and other electric or electronic component, as long as the magnetic property is not part of the intended learning or play pattern for the toy. The second is an exception for magnetic components in toys that are advanced magnetic electrical experimental kits intended for children eight years of age or older, where the kit has a warning on its container and instructions regarding the danger of swallowing magnets.
Other minor amendments not specifically related to magnets
A minor amendment is made to the definition of a toy in section 1 of the Regulations. The amendment adds an upper age reference within the existing definition to clarify its scope. Health Canada’s long-standing policy is to interpret the term “toy” as applying to toys intended for use by children under 14 years of age,footnote 27 which is consistent with the definition of toy in the Phthalates Regulations under the CCPSA. This upper age reference for toys is consistent with that applied in the United States and the European Union as well as in ISO 8124. This amendment is expected to have no impact on the intent of the existing Regulations, costs for industry or consumers, toy safety or children’s health.
Other minor amendments described below are being made to simplify and clarify the application of the Regulations. All of these amendments are expected to have no impact on the intent of the existing Regulations, costs for industry or consumers, toy safety or children’s health.
- The clause “that is intended for use by a child in play” is deleted from the definition of “plush toy” and from the definition of “soft toy” since that concept already exists in the definition of “toy.”
- In subsection 37(1), to align the English version with the French version, the English text is revised to change the expression “pull and push” to “pull or push”; in addition, the subsection is revised to remove the secondary references to imperial units “(3/8 inch)” and “(10 pounds).”
- Subsections 37(2) and 38(3) of the Regulations are deleted, since the meaning of “toy” is already defined in section 1.
Coming into force
The amendments will come into force six months after they are published in the Canada Gazette, Part II, during which time the current Regulations will continue to apply to all toys sold, advertised, imported or manufactured in Canada. The provisions of the CCPSA regarding danger to human health or safety will continue to apply to dangerous magnetic toys.
Regulatory and non-regulatory options considered
Option 1: Status quo
Paragraphs 7(a) and 8(a) of the CCPSA provide Health Canada with the authority to stop the supply of consumer products that pose a danger to human health or safety. Since 2013, Health Canada has considered certain magnetic toys to pose a danger to human health or safetyfootnote 28 and has taken action using this authority. However, this policy was not reflected in the Regulations, and in the absence of accessible and transparent rules, some industry members may not have been aware of the extent of their obligation to make their magnetic toys safe. Thus, this was not the preferred option.
Option 2: Incorporate by reference requirements set out in sections of ASTM F963
Health Canada considered an option to directly reference the full suite of magnet-related definitions, requirements, tests and warnings from the ASTM F963 standard. This option was rejected to allow for the use of consistent terminology across the amendments and the existing Regulations and to respect Canadian regulatory drafting conventions.
Option 3: Inform and educate consumers
The effectiveness of consumer information and education efforts varies with the receptiveness of the population at the time of a communication’s release, the type of media used to convey the information, the extent of media pick-up, the consumer’s ability to understand a hazard and to implement effective hazard control measures, as well as other variables.
The serious and hidden ingestion hazard posed by small powerful magnets cannot be effectively addressed by parents and caregivers alone. A further consideration is that the hazard involves older children who receive less direct supervision than younger, more vulnerable children. Therefore, Health Canada had already signalled to industry that the sale of toys that do not meet international safety standards regarding the use of small powerful magnets is prohibited in Canada. The Department will continue to supplement the amendments with information and education to consumers.
Option 4: Set out specific requirements and tests for magnetic toys in the Regulations
Option 4 is the preferred option and it is reflected in the amendments which introduce requirements, labelling and tests for magnetic toys and magnetic toy components within the Regulations under the CCPSA. Updating the Regulations by incorporating specific requirements and tests consolidates all magnetic toy requirements in an accessible, transparent and consistently applied manner. The amendments are aligned with the mandatory requirements in place in the United States and the European Union; thus, the impact on industry is expected to be low.
The amendments incorporate by reference certain test method sections from the ASTM F963 standard. In this way, magnet-related test results for toys destined for the market in the United States can be applied to toys destined for the Canadian market.
Benefits and costs
A cost-benefit analysis (CBA) that quantified the expected costs and benefits of the amendments was completed in preparation for publication of the proposal in the Canada Gazette, Part I. It is available on request to the Departmental contact.
Costs
As part of the CBA, consultations were held with businesses involved in the manufacture, import, wholesale distribution, and retail sale of children’s toys to gather estimates of the costs of adopting the amendments. Fifteen of the twenty-six businesses contacted provided input on the cost analysis. The major findings were as follows:
- Four of the five manufacturers providing input suggested they would face no costs as a result of the amendments. One small Canadian toy manufacturer identified four products that would entail redesign costs.
- All three importers providing input reported they would face no costs. However, one importer of a large volume of toys containing small powerful magnets indicated this view was based on the presumption that the toys were already compliant. If this company actually had to bear compliance costs, the results of this CBA could shift.
- All seven retailers providing input to the study reported that they would not face additional costs from the amendments.
Estimates were made of incremental product redesign costs and product testing costs associated with the amendments. Only one Canadian manufacturer indicated they expected additional costs and estimated a one-time product redesign cost of $50,000 and annual product testing costs of about $6,500. No incremental costs will be incurred by Health Canada, as the costs to administer, promote and enforce the amended Regulations will become part of Health Canada’s existing compliance and enforcement program for consumer products. Health Canada will not incur any incremental capital or operating costs due to the amendments. The total 10-year costs of the amendments were estimated to be approximately $94,610 (present value, 2016 price level).
Small businesses were asked whether a flexible regulatory option involving a six-month delay in requiring compliance would reduce costs. The one small business that identified a potential impact suggested that no cost savings would be derived from a six-month delay.
Benefits
The CBA assessed the benefits of the amendments using available information. The CBA confirmed that complete information on the number of past non-fatal and fatal injuries involving small powerful magnets in toys was not available. In order to assess benefits, the best available Canadian information on injuries involving magnets provided by CHIRPP was used. The data covered approximately 72 months, spanning January 2005 through December 2010. Notably, the data
- did not clearly identify the origin and characteristics of magnets that resulted in emergency room visits;
- represented an unknown share of all Canadian injuries since it was based on reports from only 16 Canadian hospital emergency rooms; and
- was at least six years old and did not necessarily reflect current or future injury rates.
The CHIRPP data was reviewed, filtered and grossly extrapolated to the national level. A total of about 20 injuries per year from small powerful magnets in toys was estimated. In addition, it was estimated that the annual risk of a fatality involving a small powerful magnet in a toy in Canada was about 0.005 (i.e. one fatality every 200 years).
Assumptions were made with respect to the severity and unitary costs of non-fatal injuries, the cost of a fatality, and the effectiveness of the amendments in reducing injuries and fatalities. It was estimated that the total 10-year benefits of the amendments would be approximately $2.4 million (present value, 2016 price level).
Accounting statement
The CBA for the amendments provided the accounting statement for 10 years, from 2017 to 2026, as shown in Table 2 below. The statement shows annualized average net benefits of approximately $300,000. Several additional benefits were identified but not monetized, and these are listed in the accounting statement under “Qualitative impacts.”
Table 2. Accounting statement for 2017 to 2026
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
2020 |
2026note a |
Total (PV)note b |
Annualized Average |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
A. Quantified impacts (CAD$, 2016 price level)note b |
|||||||
Benefits to consumers |
331,225 |
335,200 |
339,222 |
343,293 |
368,763 |
2,439,912 |
347,389 |
Costs to toy industry and consumers |
56,500 |
6,578 |
6,657 |
6,737 |
7,237 |
94,610 |
13,470 |
Net benefits |
274,725 |
328,622 |
332,565 |
336,556 |
361,526 |
2,345,302 |
333,918 |
B. Quantified impacts not monetized |
|||||||
Positive impacts |
None |
||||||
Negative impacts |
None |
||||||
C. Qualitative impacts |
|||||||
Positive impacts |
|
||||||
Negative impacts |
|
||||||
Sensitivity analysis
A sensitivity analysis was completed as part of the CBA. It demonstrated that if the present value of costs is five times higher than estimated and the present value of benefits is 80% lower than estimated (which could reflect a situation where the majority of magnetic toys on the market already meet the requirements outlined in Health Canada’s policy), a small net benefit of $15,000 over 10 years is still estimated.
“One-for-One” Rule
The “One-for-One” Rule does not apply, since the amendments to the Regulations do not impose any administrative costs on industry.
Small business lens
The small business lens does not apply because the estimated nationwide cost impact is less than $1 million per year and it has been determined that small business costs are not disproportionally large. The amendments are not expected to have a disproportionate effect on small businesses, given the length of time that businesses have had to manufacture and source toys that meet the policy distributed in 2013. The amendments are not expected to increase or decrease the administrative burden on small businesses, because there are no reporting or record-keeping requirements related to the amendments.
Gender-based analysis plus
The amendments to the Regulations take into consideration that the small powerful magnet ingestion incident characteristics and injury pathways are the same for all children. The amendments help to protect children under 14 years of age from magnet ingestion hazards when they play with magnetic toys irrespective of their height, weight, age or gender. There is no additional cost associated with gender-based considerations.
Consultation
In November 2009, Health Canada conducted a consultation on a proposed set of amendments to modernize Canada’s safety requirements for children’s toys under the Hazardous Products (Toys) Regulations. One of the five subjects of the consultation focused on adding requirements for magnetic toys. The consultation document was posted to the Health Canada website on November 13, 2009. It was distributed via email to stakeholders and via the Health Canada “Consumer Product Safety News” online service to more than 7 000 subscribers. Interested parties were invited to provide comments on the proposed amendments within 60 days.
Specific responses to the magnetic toy portion of the consultation were received from the following eight distinct groups: one trade association, one retail establishment, two safety advocates, two product-testing laboratories and two manufacturers. The proposed amendments for magnetic toys were well received by the respondents. There was support for aligning the Canadian requirements with those of the United States or the European Union, so that another safety standard would not be developed.
Canada Gazette, Part I, consultation
The Regulations Amending the Toys Regulations (Magnetic Toys) were published on November 4, 2017, in the Canada Gazette, Part I, for a 75-day consultation period, which ended on January 17, 2018.
A number of mechanisms were used to inform stakeholders of the publication and to invite them to submit comments on the proposal:
- On November 3, 2017, Health Canada issued a bilingual press release announcing the publication of the proposed amendments and soliciting feedback on the proposal.
- On November 3, 2017, a brief description of the proposed amendments, a link to the publication and a request for comments was added to the Government of Canada’s “Health-related consultations” web page, in English and French.
- On November 3, 2017, direct bilingual email notifications providing a link to the publication were sent to
- approximately 15 800 subscribers of Health Canada’s “Consumer Product Safety News,” and
- approximately 1 810 subscribers of the CCPSA News.
- On November 6, 2017, a bilingual message was sent by email to over 600 stakeholders (industry associations, industry members, public health stakeholders and consumers). The message informed these stakeholders of the proposed amendments and the instructions for submitting comments. Recipients were encouraged to forward the email to other interested parties.
- On November 6, 2017, Global Affairs Canada issued a notification, in English and French, of the proposed amendments according to the standard procedures for notification of the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade Committee.
Feedback from stakeholders
In total, five stakeholders submitted questions (2) or submissions (3) on the proposed amendments. Questions were received from a consumer product safety consultant (1) and a toy industry association (1). Submissions were received from a consumer (1), a consumer product safety consultant (1) and two toy industry associations who submitted jointly (1).
The industry associations’ submission and the consumer product safety consultant’s submission indicated general support for the proposal to set out requirements and tests for magnetic toys directly within the Regulations. The consumer’s submission demonstrated some misunderstandings of the proposal, but general support. The industry associations’ submission specifically indicated support for Health Canada’s efforts to align requirements and tests with the ASTM F963 standard, but noted that the 4.45 N force in the existing small parts test in the Regulations does not align with the test for small parts in toy safety requirements in other jurisdictions. The product safety consultant’s submission, while supportive of the amendments to the Regulations, suggested that a new regulation be made to set out appropriate requirements for dangerous magnets that may be present in other consumer products that could be accessible to a child. This stakeholder also suggested adding requirements to specify the location, contrast and font characteristics for the warning required on certain advanced magnetic electrical experimental kits.
Health Canada response
Health Canada carefully considered all input received and no changes to the proposed amendments were made.
Regarding the 4.45 N force in the small parts test, this force is applied to identify parts that are easily compressible and can be totally enclosed in the small parts cylinder with the application of a small force. The force application has been set out in the small parts test of the Toys Regulations since 1974. A small force is used in the test because Health Canada recognizes that even very young children apply forces to objects through the actions of pressing, chewing, sucking and swallowing. Any of these actions may enable a child to reduce the size of a compressible item in their mouth such that it can become small enough to swallow, inhale or block an airway. Thus, the 4.45 N force in the small parts test helps to further protect young children from ingestion and choking hazards when they use toys. The 4.45 N force application in the size assessment of a magnetic toy or magnetic toy component is particularly relevant for compressible toys or components (for example a small soft toy that has an embedded magnet). However, when the force is applied to a toy or toy component made of rigid material, it is unlikely that it will produce different results in the small parts test.
The suggestion to add requirements to specify the location, contrast and font characteristics for the warning required on certain advanced magnetic electrical experimental kits was not accepted. Rather, a flexible approach is utilized in order to reduce barriers to trade, given that there are different approaches adopted for warning labels across the EN 71-1, the ISO 8124-1 and the ASTM F963 toy safety standards. Canada’s approach requires critical safety information on the kit’s container and within its instructions for use. This aligns with the general approach used in other toy safety standards and should reduce barriers to trade without compromising safety.
Health Canada provided responses to all comments received to all of the commenters. The responses were sent by email in March 2018.
Regulatory cooperation
The amendments align the safety requirements for magnetic toys between Canada and the United States. Although there are pre-existing differences, such as the broader definition of “toy” in Canada and the application of a 4.45 N force for the small parts test in Canada, the amendments are aligned with the requirements and tests for magnetic toys in the United States except in the number of attach-detach cycles in the integrity tests. The ASTM F963 standard calls for two sets of 1 000 attach-detach cycles, whereas the amendments call for two sets of 10 attach-detach cycles.
Health Canada’s internal testing in 2009 demonstrated that the “impact test for magnets” in the testing sequence (see “Description” section above) was the most effective test in demonstrating magnet separation in toys known to release magnets during play. For this reason, the amendments align with the EN 71-1 and ISO 8124-1 standards and apply a more efficient two sets of 10 attach-detach cycles instead of the two sets of 1 000 attach-detach cycles. However, noting the pre-existing differences across the jurisdictions, the attach-detach tests for magnets would not have to be repeated if the 1 000 attach-detach cycle tests had already been applied according to the requirements in the United States.
Rationale
Health Canada advised manufacturers, importers and sellers of children’s toys in 2013 that the Department considers certain magnetic toys to be a danger to human health or safety and that they are therefore prohibited for sale under sections 7 and 8 of the CCPSA. However, this policy was not reflected in the Regulations, the main compendium of specific requirements for toys in Canada. The regulatory amendments incorporating requirements and tests will now consolidate all magnetic toy requirements in an accessible, transparent and consistently applied manner. These amendments help to protect children from a risk of serious injury or death when they use magnetic toys. The amendments also align Canadian requirements with those in the United States and the European Union for magnets in toys.
A CBA estimated that the total 10-year net present benefits of the amendments would be approximately $2.3 million. A sensitivity analysis was completed as part of the CBA. It demonstrated that if the present value of costs is five times higher than estimated and the present value of benefits is 80% lower than estimated (which could reflect a situation where the majority of magnetic toys on the market already meet the requirements outlined in Health Canada’s policy), a small net benefit of $15,000 over 10 years is still estimated. An early consultation on the proposal, in 2009, and the 2017 Canada Gazette, Part I, consultations were well received by stakeholders. The impact on industry is expected to be very low since mandatory safety requirements for magnetic toys have been in place for several years in the United States and the European Union, and the amendments are aligned with the requirements in those jurisdictions and with Health Canada’s existing policy.
Implementation, enforcement and service standards
The amended Regulations will not result in any major changes to Health Canada’s enforcement activities. Compliance and enforcement will be facilitated by clearly worded requirements and tests set out in the amended Regulations.
Compliance and enforcement of the amended Regulations will follow established Health Canada approaches and procedures, including sampling and testing of products, inspection at retail, follow-up on complaints made by the Canadian public and public health organizations, and follow-up on mandatory incident reports by industry. Non-compliant products will be subject to the actions available to Health Canada inspectors and other officials and will depend on the seriousness of the circumstances. These actions may include a voluntary commitment to product correction by industry, negotiation with industry for the voluntary removal of non-compliant products from the market, seizure, orders for recall or other measures, administrative monetary penalties, and prosecution under the CCPSA. Health Canada will also seek to maximize proactive compliance with the amended Regulations through ongoing industry and retailer education, and maximize safe use of magnetic toys through consumer outreach and education.
Contact
Sylvia Weihrer
Consumer Product Safety Directorate
Healthy Environments and Consumer Safety Branch
Health Canada
Address locator: 4908B
269 Laurier Avenue West
Ottawa, Ontario
K1A 0K9
Fax: 613-952-2551
Email: sylvia.weihrer@canada.ca